Exploring the difference and relationship between Crystals and Oscillators
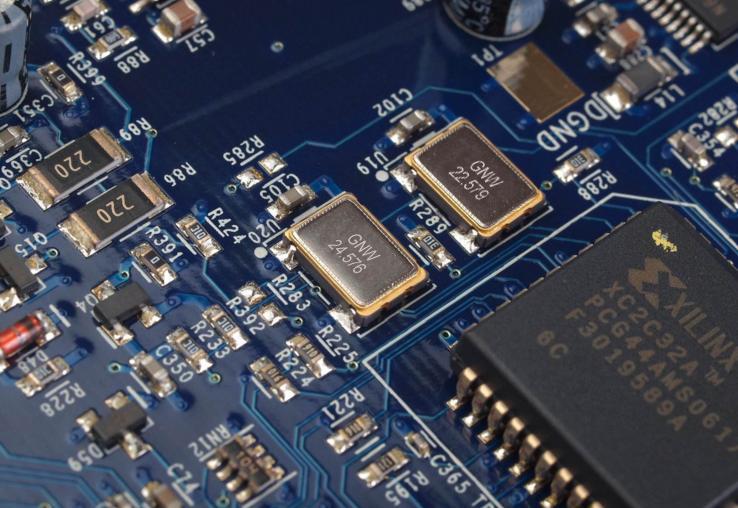
Crystals and Oscillators are important components in electronic devices that provide a stable clock signal for the proper operation of circuits.
Now let's first look at the differences between crystals and oscillators.
From a functional point of view, crystals work primarily on the basis of their piezoelectric effect and have the unique ability to vibrate at a specific frequency when an electric field is applied. An oscillator, on the other hand, is a circuit system that generates oscillating electronic signals, usually using active devices such as transistors to establish and maintain a stable oscillation frequency.
Structurally, crystals are usually made of quartz and are simple and compact in design. Crystals usually have two to six pins inside for connection to electronic circuits. Oscillators, on the other hand, are more complex electronic components and are usually labelled with an output frequency for user selection and identification. Oscillators typically have four pins, two for the input power supply, one for the output signal and one which may be unused or used for other functions such as a reference output.
Despite the differences between crystals and oscillators, they are closely related and work together to ensure the proper operation of electronic equipment. They work together to provide a stable clock signal, with the crystal determining the base frequency of the oscillator. This stable clock signal is essential for the synchronised operation of the various components in the circuit. In addition, the combination of crystal and oscillator is critical to maintaining the accuracy and precision of timing in electronic systems, which is essential for applications such as data transmission.
In summary, although their differences in function and design, quartz crystals and oscillators complement each other in electronic devices and work together to ensure the proper functioning of circuits. Understanding these differences and relationships will help engineers and technicians better select and use these two components to fulfil their important roles in electronics.